Introduction
In this blog post, I explain how you can configure your SQL Developer to highlight hints and distinguish them from ordinary comments. The SQL Language Reference for Oracle Database 19c defines hints as follows:
Hints are comments in a SQL statement that pass instructions to the Oracle Database optimizer. The optimizer uses these hints to choose an execution plan for the statement, unless some condition exists that prevents the optimizer from doing so.
Furthermore
A statement block can have only one comment containing hints, and that comment must follow the
SELECT,UPDATE,INSERT,MERGE, orDELETEkeyword.
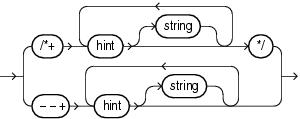
And here’s the syntax diagram:
You see the comment containing hints starts with a +. The syntax for a hint is simplified. string must be read as a placeholder for various hint-specific options. You find a list of officially supported hints in the SQL Language Reference.
In this blog post, I covered how syntax highlighting works in SQL Developer and how to add a custom styler. If you are interested in the details, then I recommend reading this blog post first.
The Problem
A custom styler written in Arbori works with nodes provided in the parse-tree (target). However, the parse-tree does not contain whitespace nor comments. We still have access to the source code through the parse-tree (target.input) and therefore to all comments. For example, by creating a token stream via LexerToken.parse(target.input, true) and looking for tokens of type LINE_COMMENT and COMMENT. That’s not the problem.
The problem is, that there is no functionality to style a token. We only can style a node by calling struct.addStyle(target, node, 'MyStyle'). We cannot highlight hints with this method.
Let’s dig deeper.
The global variable struct is an instance of the CustomSyntaxStyle class. Here’s an excerpt based on the representation in IntelliJ IDEA:

The excerpt shows the complete implementation of the addStyle method. The tokens of the passed node are added to a local field named styles. This field is defined on line 33 without an access modifier and therefore it is not accessible by the Arbori program.
What can we do?
The Approach
We cannot solve the problem. Only the SQL Developer team can. But we can work around it. We can access the hidden field styles through Java reflection. Have a look at this excellent tutorial by Jakob Jenkov, if you want to learn more. We will use this approach in the Arbori program.
The Arbori Program to Highlight Hints
This Arbori program applies the style Hints for all hints within a worksheet or PL/SQL editor. I’ve tested it successfully with SQL Developer 19.2, 19.4 and 20.2.
Hints:
[node) sql_statements
-> {
var getHints = function() {
var LexerToken = Java.type('oracle.dbtools.parser.LexerToken');
var Token = Java.type('oracle.dbtools.parser.Token');
var tokens = LexerToken.parse(target.input, true);
var hints = [];
var prevToken = tokens[0];
for (var i=1; i<tokens.size(); i++) {
if ((tokens[i].type == Token.LINE_COMMENT || tokens[i].type == Token.COMMENT) && tokens[i].content.length > 3) {
if (tokens[i].content.substring(2, 3) == "+") {
var prev = prevToken.content.toLowerCase();
if (prev == "select" || prev == "insert" || prev == "update" || prev == "delete" || prev == "merge") {
hints[hints.length] = tokens[i];
prevToken = tokens[i]
}
}
}
if (tokens[i].type != Token.WS && tokens[i].type != Token.LINE_COMMENT && tokens[i].type != Token.COMMENT) {
prevToken = tokens[i];
}
}
return hints;
}
var styleHints = function(hints) {
var Service = Java.type('oracle.dbtools.util.Service');
var Long = Java.type('java.lang.Long');
var stylesField = struct.getClass().getDeclaredField("styles");
stylesField.setAccessible(true);
var styles = stylesField.get(struct);
for (var i in hints) {
var pos = new Long(Service.lPair(hints[i].begin, hints[i].end));
styles.put(pos, "Hints");
}
}
// main
styleHints(getHints());
}Here are some explanations:
- On line 2 we query the root node containing all
sql_statements. As a result, we call the JavaScript on line 3 to 41 only once. - The main program starts on line 40. It collects all hints by calling the local function
getHints()and styles them by calling the local functionstyleHints(). - We populate all tokens including whitespace and comments on line 7.
- We add tokens (relevant comments containing hints) to the result list on line 15.
- On line 32 we provide the invisible field
stylesof thestructobject as a variablestyleswith the help of the Java Reflection API. - On line 34 the start and end position of a token is converted to a
Longvalue. This value identifies a token in the editor. - And finally, we apply the style
Hintsto all hint tokens on line 35.
Register Style Hints
Add the the Arbori program Hints to the PL/SQL custom Syntax Rules in the preference dialog as shown below:

Save the preferences by pressing the OK button and then restart SQL Developer. This is necessary to register the new custom Style Hints.
Then, after restarting SQL Developer, open the preferences dialog again and configure the style Hints the way you want.

The Result
In the next screenshot, you see a simple query with two syntactically correct hints. However, as mentioned in the introduction only the first comment containing hints is considered by the Oracle Database and therefore highlighted in red.

The second query produces the execution plan including a hint report for the first query. As you see, only the first hint full(e) is used and the second hint full(d) is ignored. The second hint is not reported. It is an ordinary comment after all.
1 Comment
[…] this blog post, I explained how you can distinguish hints from ordinary comments and highlight them in SQL […]